
| Product Name | Status | Description | Features | Package | Q-Level |
| Si4386DY | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.007Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.0095Ω@4.5V; Qg=11nC | SMD SO-8 | ||
| Si4634DY | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0052Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.0067Ω@4.5V; Qg=21.5nC | SMD SO-8 | ||
| Si4660DY | N-Channel 25-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0058Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.007Ω@4.5V; Qg=17nC | SMD SO-8 | ||
| Si7110DN | N-Channel 20-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0053Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.078Ω@4.5V; Qg=14nC | SMD PowerPAK 1212-8 | ||
| Si7114DN | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0075Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.010Ω@4.5V; Qg=12.5nC | SMD PowerPAK 1212-8 | ||
| Si7686DP | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0095Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.014Ω@4.5V; Qg=9.2nC | SMD PowerPAK SO-8 | ||
| Si7804DN | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0185Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.030Ω@4.5V; Qg=8.7nC | SMD PowerPAK 1212-8 | ||
| SiE822DF | N-Channel 20-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0034Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.0055Ω@4.5V; Qg=24nC | SMD PolarPAK | ||
| SiE844DF | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.007Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.010Ω@4.5V; Qg=13.1nC | SMD PolarPAK | ||
| SiR402DP | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.006Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.008Ω@4.5V; Qg=14nC | SMD PowerPAK SO-8 | ||
| SiR462DP | N-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0079Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.0095Ω@4.5V; Qg=8.8nC | SMD PowerPAK SO-8 | ||
| SiR892DP | N-Channel 25-V (D-S) MOSFET | RDS(on)=0.0032Ω@10V; RDS(on)=0.0042Ω@4.5V; Qg=20nC | SMD PowerPAK SO-8 |

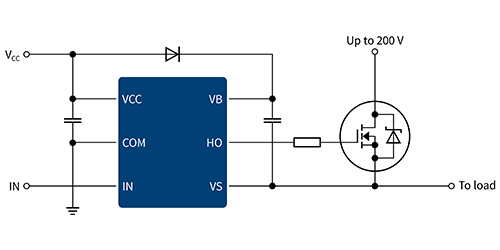
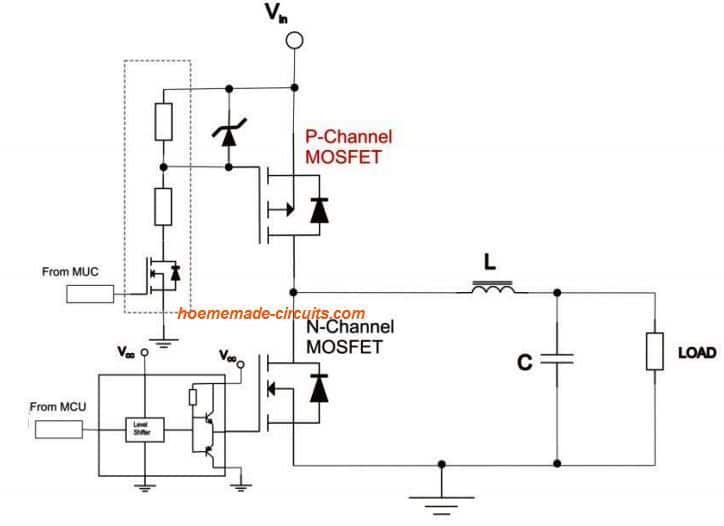
But for high side switching you can use a P-channel enhancement mode MOSFET where the off gate voltage is equal to the load supply voltage and the on gate voltage is ground/0V. The only problem then is if the gate drive circuit works on a lower voltage than your load e.g. A 3.3V microcontroller driving a 12V load. The MAX1614 drives high-side, n-channel power MOSFETs to provide battery power-switching functions in portable equipment. The n-channel power MOSFETs typically have one-third the on-resistance of p-channel MOSFETs of similar size and cost. There is a gotcha with the high-side switch; if the V D D feeding into the MOSFET is more than about 0.6v higher than the supply voltage for the microcontroller, it can damage the latter. This would occur, for example if you are running a microcontroller at 5V and are switching 12V with the high-side switch. Mosfet high side driver you can use from the high rail a resistor connected to the high side FET gate. Then the collector of an NPN transistor whose emitter is to ground. Drive the base from your logic through a series resistor. MOSFET DRIVER, HIGH/LOW SIDE, SOIC-8, Device Type:MOSFET Driver, IC Generic Number:2104, Peak Output Current:360mA, Product Range:-, of Outputs:2Outputs, Logic Function Number:2104,Driver Case Style:SOIC, IC, Top Selling Products Excellence quality Large online sales Best retailers with a.
High Side Mosfet Switching

MOSFET Switches - Learn About Electronics
